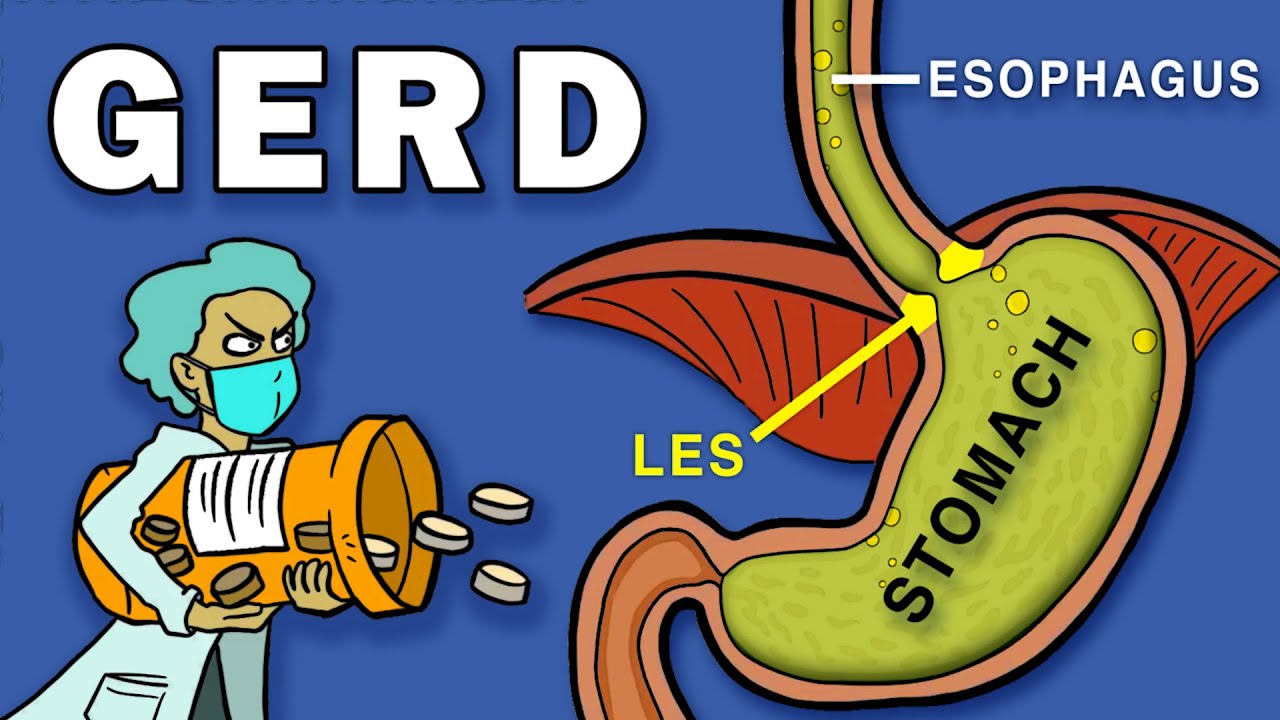
 Gastroesophageal reflux disease, also known as GERD or acid reflux, is a chronic condition in which stomach contents rise and enter the esophagus. This occurs due to problems with closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, or LES, which is the junction between the stomach and esophagus. The most common symptoms are a burning sensation in the chest called heartburn, regurgitation, and an acidic taste in the back of the mouth. Heartburn typically occurs after eating and may worsen at night. Less commonly, people may experience dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing. Dysphagia can manifest as pain when swallowing, a sore throat, choking, coughing, gurgling or regurgitating food or stomach acids, feeling that food is stuck behind your breastbone, a burning sensation behind your breastbone, and hoarseness. There may also be nausea, frequent burping, chest pain, the sensation of a lump in your throat, wearing away of teeth, and bad breath. GERD can cause a recurrent cough, breathing difficulties, chest congestion, and lung inflammation leading to asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, also known as GERD or acid reflux, is a chronic condition in which stomach contents rise and enter the esophagus. This occurs due to problems with closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, or LES, which is the junction between the stomach and esophagus. The most common symptoms are a burning sensation in the chest called heartburn, regurgitation, and an acidic taste in the back of the mouth. Heartburn typically occurs after eating and may worsen at night. Less commonly, people may experience dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing. Dysphagia can manifest as pain when swallowing, a sore throat, choking, coughing, gurgling or regurgitating food or stomach acids, feeling that food is stuck behind your breastbone, a burning sensation behind your breastbone, and hoarseness. There may also be nausea, frequent burping, chest pain, the sensation of a lump in your throat, wearing away of teeth, and bad breath. GERD can cause a recurrent cough, breathing difficulties, chest congestion, and lung inflammation leading to asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia. Complications that can occur from it include esophagitis, or inflammation of esophagus, esophageal stricture, in which scar tissue develops and narrows the esophagus, and Barrett’s esophagus, in which the lining of the esophagus comes to resemble tissue that lines the intestines – which can lead to cancer.
Risk factors for GERD include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, and certain medications. Hence, treatments include lifestyle changes such as losing weight and quitting smoking. Other lifestyle changes include eating several small meals a day instead of 3 big meals, avoiding food resulting in symptoms, not lying down 2-3 hours after eating, and raising the head of the bed. Foods that can exacerbate GERD symptoms include spicy, fatty, or fried foods, garlic, onions, citrus fruits, tomatoes, caffeine, and fizzy drinks.
There are also medications that can be used to treat GERD symptoms. These include proton pump inhibitors, or PPIs, and histamine-2 (or H2) receptor blockers, both of which reduce stomach acid production. There are also prokinetics, which cause the stomach to empty more quickly, antacids, which neutralize acid in the stomach, and medications that strengthen the LES.
Some people still have symptoms interfering with their quality of life despite lifestyle changes and taking medication. Still others wish to avoid taking medication long-term. In such cases, surgeries can be performed to reinforce and strengthen the LES. The most common of these is Nissan fundoplication. In this surgery, the stomach’s fundus is wrapped around the LES. During a total fundoplication, the fundus is wrapped 360 degrees around. In a partial fundoplication, the fundus is not wrapped completely around the stomach. Some people with GERD may have a hiatal hernia, which is when part of the stomach slips through the diaphragm into the middle compartment of the chest. If a hiatal hernia is present, that is also fixed during the surgery.
Asthma and GERD frequently occur together. The reason is not certain, but it is believed that acid flowing from the stomach injures the throat lining, airways, and lungs. Another potential cause could be that when acid enters the esophagus, a nerve reflex kicks in and constricts airways to keep acid out. This can result in shortness of breath.

0 Comments